Diagnostic Testing
|
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT) An activated partial thromboplastin time measures the intrinsic pathway of coagulation. It will detect abnormally low levels of activity of factors XII, XI, X, IX, VIII, V, II, and I. The test is run on plasma that is drawn in a tube containing sodium citrate. The sodium citrate removes calcium to prevent clotting. Plasma is mixed with 2 substances that initiate the intrinsic pathway of coagulation. The first is a phospholipid that acts as platelet factors (partial thromboplastin). The second is a substance that activates factor X. The final ingredient for coagulation to occur is calcium. The amount of time it takes for the plasma mixture to clot, after the addition of calcium, is called the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT). This time is compared to a normal control value. |
|
Cytochemical stains are used to identify chemical constituents within the cell. They are used primarily to differentiate the leukemias. |
|
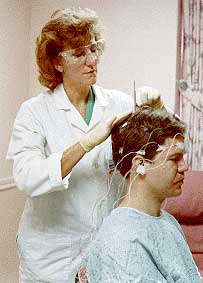
An evoked potentials test records the time it takes for a sensory stimulus, such as a light flashed into the eyes, to reach the brain. The test can check the brain's response to visual, auditory, and pain stimuli. Electrodes are simply attached to the scalp, connecting the individual to an electroencephalograph (EEG), a device that records brain waves. (Rosner's Multiple Sclerosis 49.)
|
|
Factor Assays test for the level of individual coagulation factors in the blood. Factor Assays are indicated after a prolonged PT or APTT (when a bleeding disorder is suspected and the patient is not undergoing anticoagulant therapy). Patient plasma is mixed with a substrate containing the factor being tested for. A PT or APTT is run depending on the factor being tested (PT for extrinsic factors, APTT for intrinsic factors). Results are compared to a standard with a known amount of the factor being tested for. Example: Joe Black is a hemophiliac with 1% of factor VIII present in his blood. The APTT was prolonged. When the patient's plasma is mixed with a substrate containing factor VIII, the APTT is corrected, or normal. If factor IX was mixed with the patient's plasma, the APTT would still be prolonged because the missing factor had not been added. By this process of elimination, the deficient factor can be identified. |
|
Certain antigens are expressed on cell lines at different stages of cell maturation. In leukemias, hematopoietic bone marrow cells stop development at a certain stage of maturation and then proliferate. By typing the antigen markers on leukemic cells, leukemias can be diagnosed and classified. |
|
The prothrombin time measures the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. It will detect abnormally low levels of activity of factors I, II, VII, and X. The test is run on plasma that is drawn in a tube containing sodium citrate. The sodium citrate removes calcium to prevent clotting. The extrinsic pathway of clotting depends on tissue factor (thromboplastin) to start the pathway, and calcium. 1 part of patient plasma is mixed with rabbit lipoprotein extract that contains tissue factor. Calcium chloride is added to this mixture and the test is timed. The amount of time it takes for the plasma mixture to clot, after the addition of calcium, is called the prothrombin time. This time is compared to a normal control value. |